By Beatrice Nakibuuka
Human immunity is the body’s tool to defend itself against harmful pathogens like viruses, bacteria and fungi.
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues and organs that work jointly to recognize and eliminate harmful invaders.
Dr Simon Mabike, a general physician at International Hospital Kampala (IHK), says when the immune system detects an invading pathogen, it triggers an immune response including production of antibodies and activation of immune cells.
These immune cells then work together to destroy the pathogen and prevent it from causing harm to the body.
Types of immunity
Dr Mabike says innate immunity is the first line of defense against pathogens which is produced in everyone’s body at birth.
This form of immunity includes physical barriers such as skin and mucus membranes, and specialized cells and proteins that can detect and destroy pathogens.
“Naturally, people are born with some immunity that attacks pathogens. External barriers of our bodies such as the skin and mucus membranes of the throat and gut, are the first line of defense against pathogens,” Dr Mabike says.
“If pathogens manage to bypass the innate immune system, the white blood cells will attack and kill them” he adds.
People are born with some types of immunity, but exposure to diseases and vaccinations can also help boost the body’s defense.
Adaptive immunity (active) on the other hand, develops over time.
This involves the production of antibodies and activation of immune cells that are specifically targeted to a particular pathogen.
Dr Mabike says vaccinations and exposure to various diseases help the body develop a range of antibodies to different pathogens.
“Immunizations change the body in some way so it can respond effectively to various diseases. Usually, antigens or weakened pathogens are introduced into a person’s body so the individual produces antibodies and does not become sick because the body saves copies of the antibodies. It then has protection if the threat reappears later in life,” he explains.
Passive immunity is a temporary type of immunity that is derived from another person. For instance, a newborn receives antibodies from the mother through the placenta before delivery, and in breast milk after delivery.
This passive immunity protects the infant from some infections during their early life.
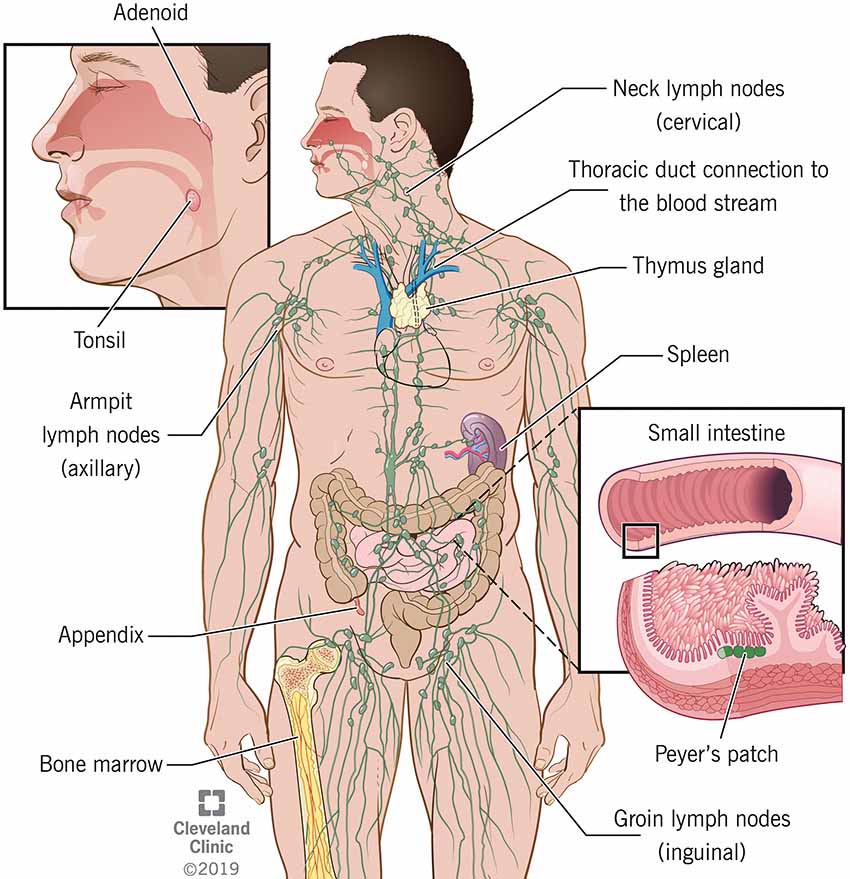
Components
The body immune system consists of these components:
The white blood cells, which are key players in your immune system. They are manufactured in the bone marrow and are part of the lymphatic system.
They move through blood and tissue throughout your body, looking for foreign invaders and when they find them, they launch an immune attack.
Antibodies help the body to fight microbes or toxins they produce by recognising substances called antigens on the surface of the microbe, or in the chemicals they produce, then mark them as foreign and thereafter, destroy them.
Immune cells gather in lymph nodes and react when antigens are present, causing swelling.
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped glands found in the neck, underarms, groin and abdomen. They link via lymphatic vessels.
The tonsils, adenoids and appendix are gateways for pathogens to enter the body. So, lymphoid tissues are located there to do the protective job.
The spleen is a blood filtering organ found at the upper left part of the abdomen. It removes microbes and destroys old or damaged red blood cells.
It also manufactures antibodies and lymphocytes which are disease-fighting components. Bone marrow is the spongy tissue found in the center of bones.
It produces the red blood cells which the body needs to carry oxygen, the white blood cells that fight infection, and the platelets which help in blood clot.
The thymus is another component of the immune system which filters and monitors blood content. This gland is a small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone.
It makes white blood cells called lymphocytes, which protect the body against infections. The body’s other defense systems against microbes include the skin, lungs and digestive tract.
The mucus lining contains antibodies and the acid in the stomach can kill most microbes, body fluids like skin oil, saliva and tears contain anti-bacterial enzymes that help reduce the risk of infection.
Fever is an immune system response, and when there is a rise in body temperature, the body triggers the repair of cells and death of some microbes.

Disorders
Dr Franklin Wasswa, a general physician at Entebbe Hospital says a fully functional immune system can distinguish healthy tissue from unwanted substances.
If it detects an unwanted substance, it will attack it to protect the body. It also recognizes and removes dead and faulty cells.
However, the immune system does not always get it right. It can go wrong and the types of immune disorders fall into three categories:
Immunodeficiency: These arise when one or more parts of the immune system do not function.
They can result from a condition that a person is born with or develop over time.
Old age, malnutrition, obesity, diseases like HIV/AIDs, or high alcohol use, medical treatment, such as chemotherapy, drugs to treat an autoimmune condition, or medications to stop the body from rejecting a transplant increase a person’s risk of becoming sick or experiencing severe symptoms.
Autoimmunity: In autoimmune conditions, the immune system mistakenly targets healthy cells rather than pathogens or faulty cells.
It does not distinguish between healthy and unhealthy cells and tissues.
Usually, this occurs in one part of the body such as the pancreas. Destruction of pancreatic beta cells means the body cannot produce insulin.
This is how type 1 diabetes happens. Other autoimmune diseases include celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and graves’ disease.
Hypersensitivity: Here, the immune system reacts in an exaggerated or inappropriate way.
It attacks substances like food or dust as if they were pathogens. This causes asthma, food allergies, and the body responds to an allergen so strongly that it can be life-threatening.
How infections enter
Infections can enter the body through various means, including inhalation, ingestion, and contact with infected fluids.
Once inside the body, pathogens can spread through the bloodstream or lymphatic system, which are both major components of the immune system.
Dr Mabike says: “Pathogens may also enter the body through cuts, wounds, or other openings in the skin. In addition, infections can spread from person to person through close contact, such as touching, kissing, or sexual intercourse.”
Once an infection enters the body, the immune system responds by sending specialized cells to the site of infection to fight off the invading pathogen.
This process can cause inflammation which may lead to symptoms such as fever, pain, and swelling. If the immune system is unable to fight the infection, it may spread to other parts of the body and cause more severe symptoms or even lead to serious complications.

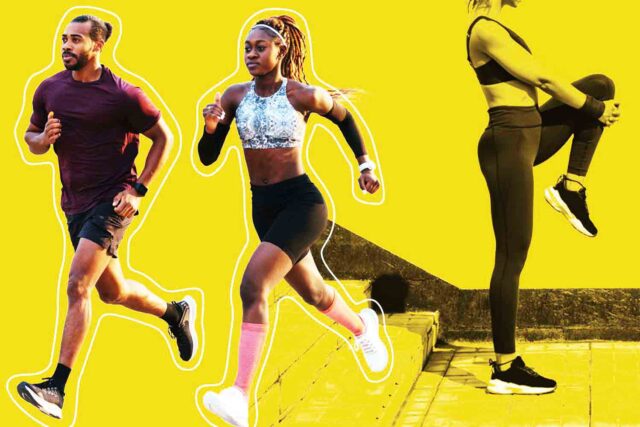
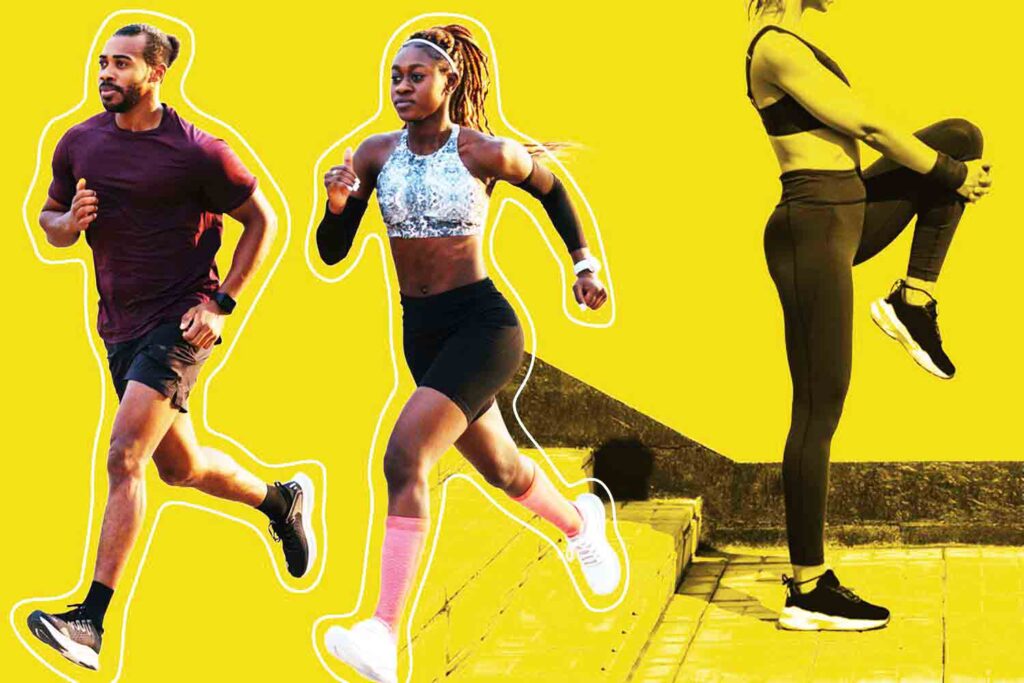
How to boost the system
According to Ivan Baguma, a nutritionist at Nella Organics in Kampala, a strong immune system is essential for maintaining good health and preventing diseases.
A weakened immune system can increase the risk of infections and diseases, including cancer.
Therefore, it is important to take care of your immune system by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, exercising regularly, and avoiding harmful substances such as tobacco and excessive alcohol.
Baguma says balancing your immune system is important to maintain your overall health and to prevent certain autoimmune conditions.
Balancing immunity
Here are some tips to help you balance your immune system:
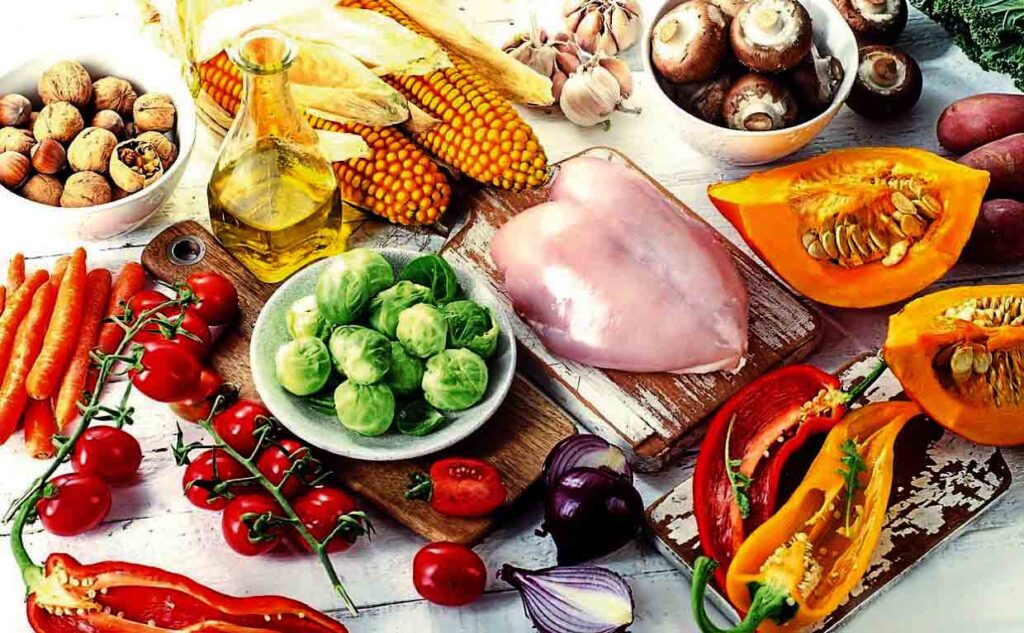
Eating healthy and balanced diet: “Make sure your diet consists of plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean protein sources, whole grains, and healthy fats. Avoid processed foods and limit sugar and alcohol intake. Eating healthy will help you maintain a healthy weight,” Baguma says.
Some superfoods which speed up recovery include turmeric, mushrooms, camu camu powder, and ginger, among others.
Those that boost immunity include super berries like elderberry, acai, and echinacea, among others.
Get enough sleep: Not having enough sleep can negatively affect different parts of the immune system, causing a variety of disorders.

Aim to get 7-9 hours of sleep per night to help keep your immune system functioning properly.
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake: Both smoking and excessive alcohol intake can weaken your immune system.
Smoking can make the body less successful at fighting diseases, and increase the risk for immune system problems such as rheumatoid arthritis. Consumption of alcohol weakens the immune system.
Baguma says: “Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of certain health conditions and weaken your immune system. Excess weight can affect how your body functions.”
Obesity, defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more in adults, is linked to impaired immune functions.
Some of the safe ways to help maintain a healthy weight includes reducing stress, eating healthy foods and engaging in regular physical exercise.
Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands frequently and properly, especially during cold and flu seasons, to reduce the risk of illness.
Manage stress: Chronic stress can weaken your immune system. Try stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga or deep breathing exercises.
Regular exercise: Exercise is not only good for physical health, but also in boosting immunity.
There are some essential oils that boost immunity. These include lemon, palmarosa, petitgrain, copaiba oleoresin, and frankincense.
Remember, balancing your immune system is not a one-time fix. It involves making lifestyle changes that will have long-term benefits for your overall health.
Taking care of yourself will help your immune system take care of you because your immunity is your defense.