By Patricia Aceng
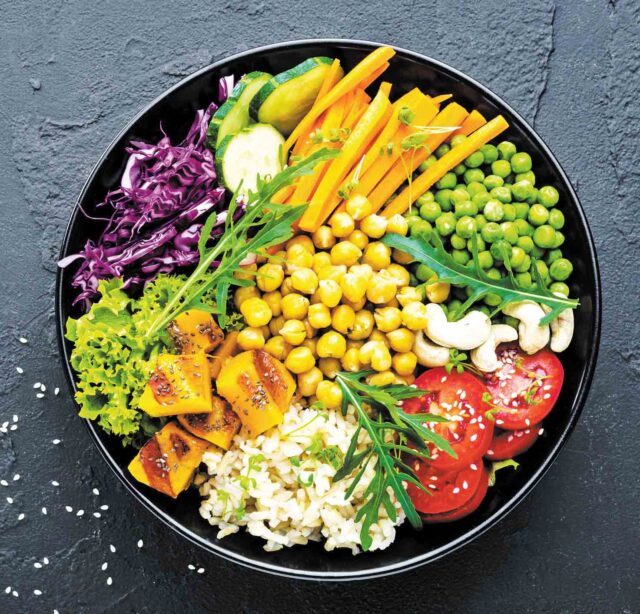
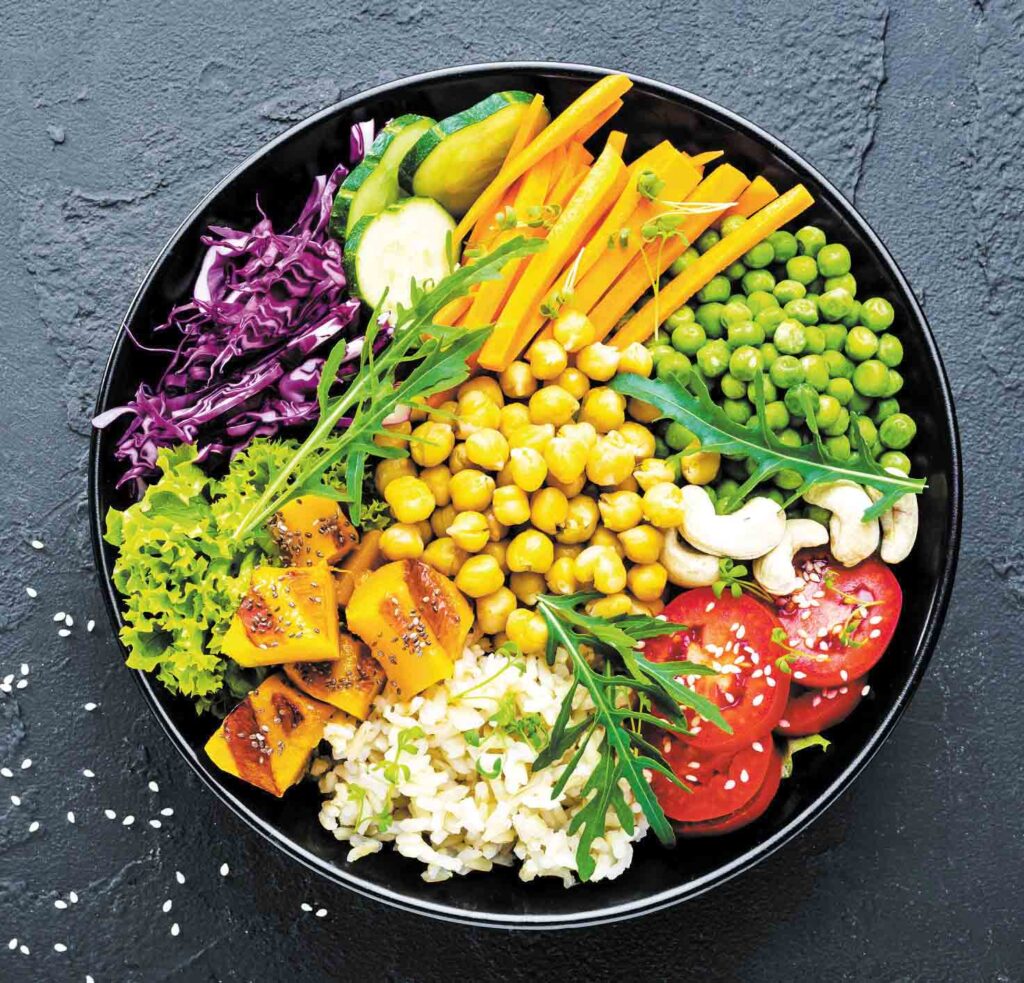
Vegetarian diet is a type of diet comprised mainly or exclusive of edible plant tissues, organs and product and excluding animal meats, poultry or seafood.
It is a meal plan made up of foods that come mostly from plants.
It consists of edible plant tissues and organs such as fruits, seeds, leaves, roots, stems, and other foods derived from plants (bread, soy and pasta).
Those who follow this kind of diet are called vegetarians. I guess you have heard friends or people with such menu plan.
It is mostly associated with health, political, ethical, and economical concern.
Nutritional inadequacy
Vegetarian diets may be associated with a reduced risk for a number of health problems such as: cardio vesicular diseases, colon cancer or excess body weight.
Compared to omnivores, vegetarians and vegans can consume greater amounts of folate, vitamin C and vitamin E.
However, without supplementation vitamin B12, calcium and zinc, intake of vegetarians may be insufficient.
Omnivores consume a variety of animal products. However, their intake of folate, magnesium, iron, calcium, vitamin E and copper can be inadequate.
Regardless of dietary focus, adults should consume a variety of foods to ensure their nutritional requirements are being met.
Studies have shown that without supplement or enriched foods, vegetarians are at a high risk of vitamin B12 deficiency.
This is because there are nutrients that are essential for a normal body functioning which are not found in plants.
Nutrients not in veges

- Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that is almost exclusively found in animal- sourced foods such as fish, meat, dairy products and eggs. Also known as cobalamin, it is a water-soluble nutrient involved in developing red blood cells and maintaining nerves and normal brain function.
Symptoms and risks associated with vitamin B12 deficiency
– Weakness and fatigue.
– Impaired brain function.
– Neurological disorder.
– Psychiatric disorder.
– Megaloblastic anemia.
– Possible links to Alzheimer’s and heart disease.
To get sufficient amount of vitamins B12, vegetarians must take supplements or eat foods that has been fortified with this nutrient. Foods like enriched yeast extracts, soy products, breakfast cereals, bread, and meat substitutes. - Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol)
Vitamin D3 is an essential nutrient with very many important functions.
It is also called the sunshine vitamin so it does not have to come from your diet.
Your skin can get vitamin D when exposed to sunlight. However, if your sunlight exposure is limited or you live far from equator, you must get it from food or supplement.
There are two types of dietary vitamin D namely: Ergocalcifero (D2), found in plants and Cholecalciferol (D3) found in animal-based foods.
Of these two types, cholecalciferol (D3) increases blood levels of absorbable vitamin D much more efficiently than Ergocalciferol (D2) and the best sources of vitamin D3 are: fatty fish, and egg yolks.
Other sources include supplements, cod liver oil, or enriched foods like milk or cereals.
Deficiency signs
Osteoporosis, with increased risks of fracture in older adults.
– Cancer.
– Heart disease.
– Depression.
– Muscle wasting and reduced strength especially in older adults.
Since vitamin D3 is a type of vitamin D found in animal sourced foods, especially fatty fish and more effective at raising blood levels of vitamin D than plant forms of vitamin D, vegetarians may be at a higher risk of deficiency hence need supplementing. - Heme iron
Heme iron is a type of iron that is only found in meat, especially red meat.
It is much better absorbed than the non-heme iron, which is commonly found in plant foods.
For this reason, vegetarians especially females and people on raw food diets are more prone to anemia than the meat eaters.
However, iron deficiency is easy to avoid on well-planned vegetarian diet that contains plenty of non-heme iron. - Creatine
Creatine is a molecule found in animal foods. Most of it is stored in your muscles, but significant amounts are also concentrated in your brain.
It functions as an easily accessible energy reserve for muscle cells, giving them greater strength and endurance.
Creatine is not essential in your diet since it can be produced by the liver; however vegetarians tend to have lower amounts of Creatine in their muscles.
There is no doubt that vegetarian diets are very healthy diets and have been associated to many health benefits like reduced risks to a number of health problems.
However, one has to be acquainted with the inadequacies that vegetarian diets bid.
The writer is a nutritionist/dietitian at St Joseph’s Health Centre, Mukono).
favouredpatricia2017@gmail.com